| 23 | gI Outline of Japanese School Systemh | Previous | Next | JAPANESE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
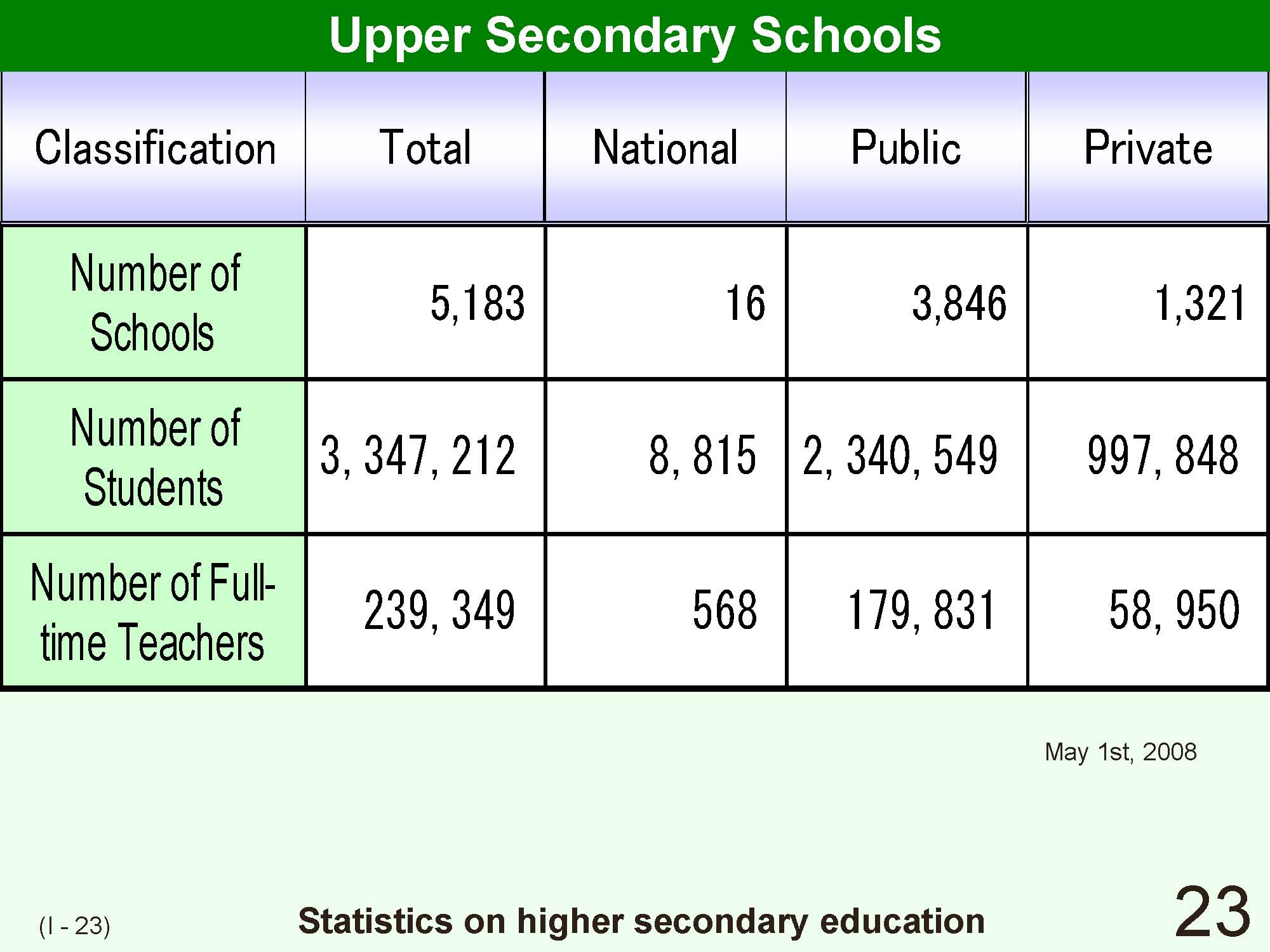
| The enrollment rates in upper secondary schools in Japan reached 97% in 2002. While the upper secondary education is not compulsory, it is regarded as equivalent to the compulsory education and has required special arrangements in order to accommodate the diverse range of students enrolled. Advanced courses (vocational courses or comprehensive courses) have diversified and have been established in the credit system in upper secondary schools. Nowadays, diverse options and flexible responses are needed due to the decreasing demand for part-time courses for working students arising from economic growth accompanied by the increasing demand for correspondence courses for school students choosing not to attend full time.
In addition, approximately 2/3rds of students proceed to the tertiary educational level consisting of universities, junior colleges and specialized training colleges. This situation demands that adapted guidance be provided that addresses studentsf interests, aptitudes and competence. |
||||
Please send your comments and concerns here
kamada@criced.tsukuba.ac.jp
Center for Research on International Cooperation in Educational Development(CRICED) University of Tsukuba
1-1-1, Tennodai, Tsukuba-shi, IBARAKI
305-857, JAPAN