| 3 | gI Outline of Japanese School Systemh | Previous | Next | JAPANESE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
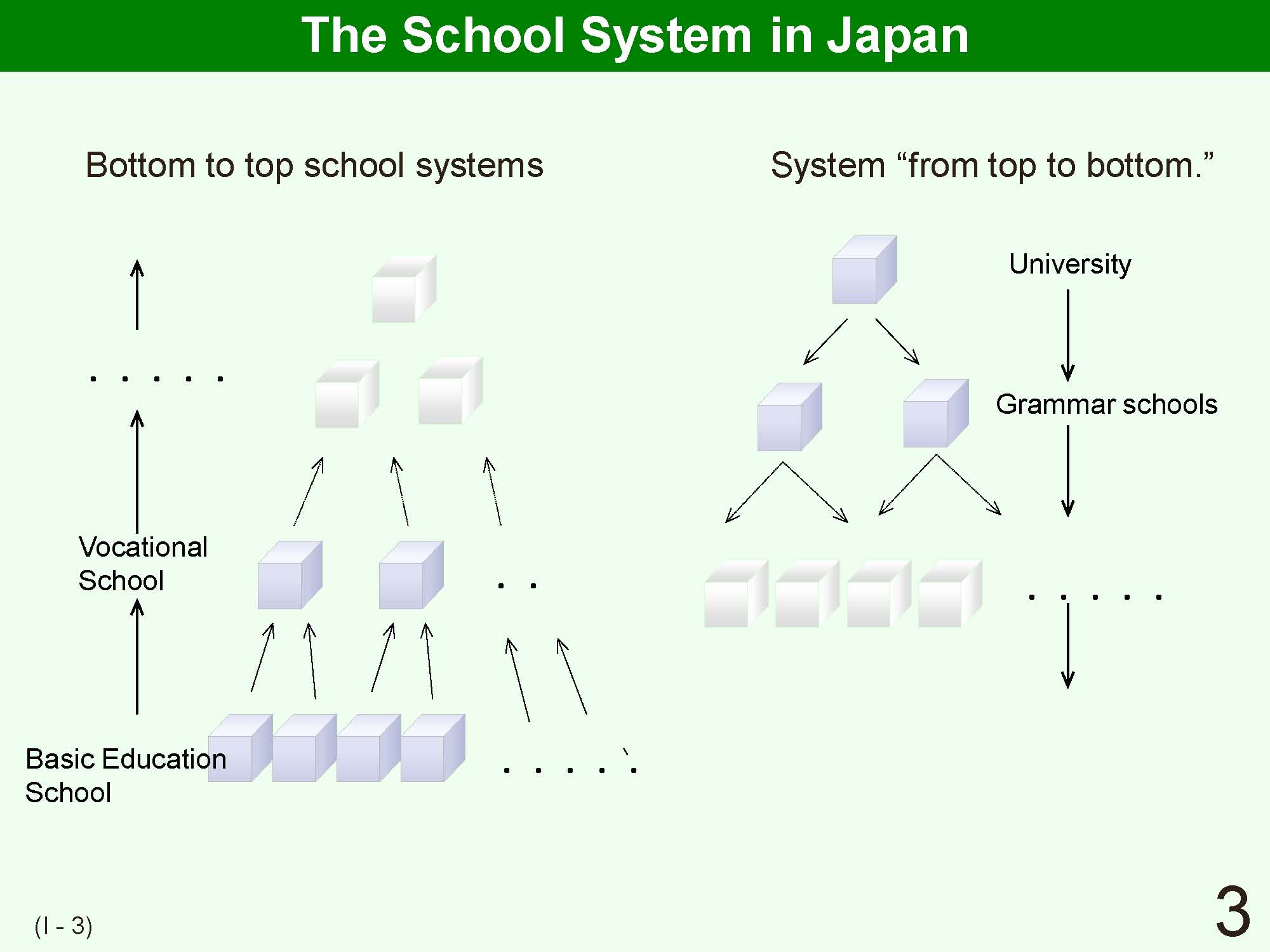
| Under the dual school system the following two systems exist at the same time. The first system is the structured system from university (the highest level of educational institutions), that is a place for the most advanced study and research, to preparatory schools(grammar schools): or a system efrom top to bottom.f The second system introduced during the modern period involves schooling for basic education, including teaching literacy to the common people. The single-track school system integrates the top-to-bottom school system with the bottom-to-top school system. Whereas the dual school system has been common in Europe historically characterized by aristocratic and hierarchical societies, the single-track school system is typical of the United States.
From the end of the 19th century to the early 20th century in Japan, following broad calls for democratization of education, the shift from the dual school system to the single-track school system was developed as a school unification movement. At first, only the elementary school levels were synthesized. During this transition period, there was a multi-channel school structure as a transitional, middle form of the two systems. Later, changes also occurred also at the secondary school level and in the basic education system, including the establishment of a lower division level of secondary schools and a shift to the single-track school system. However, what roles secondary schools, which connect compulsory and higher education, should take is a matter of perspective of the level of the educational system. |
||||
Please send your comments and concerns here
kamada@criced.tsukuba.ac.jp
Center for Research on International Cooperation in Educational Development(CRICED) University of Tsukuba
1-1-1, Tennodai, Tsukuba-shi, IBARAKI
305-857, JAPAN