| 22 | gI Outline of Japanese School Systemh | Previous | Next | JAPANESE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
||||
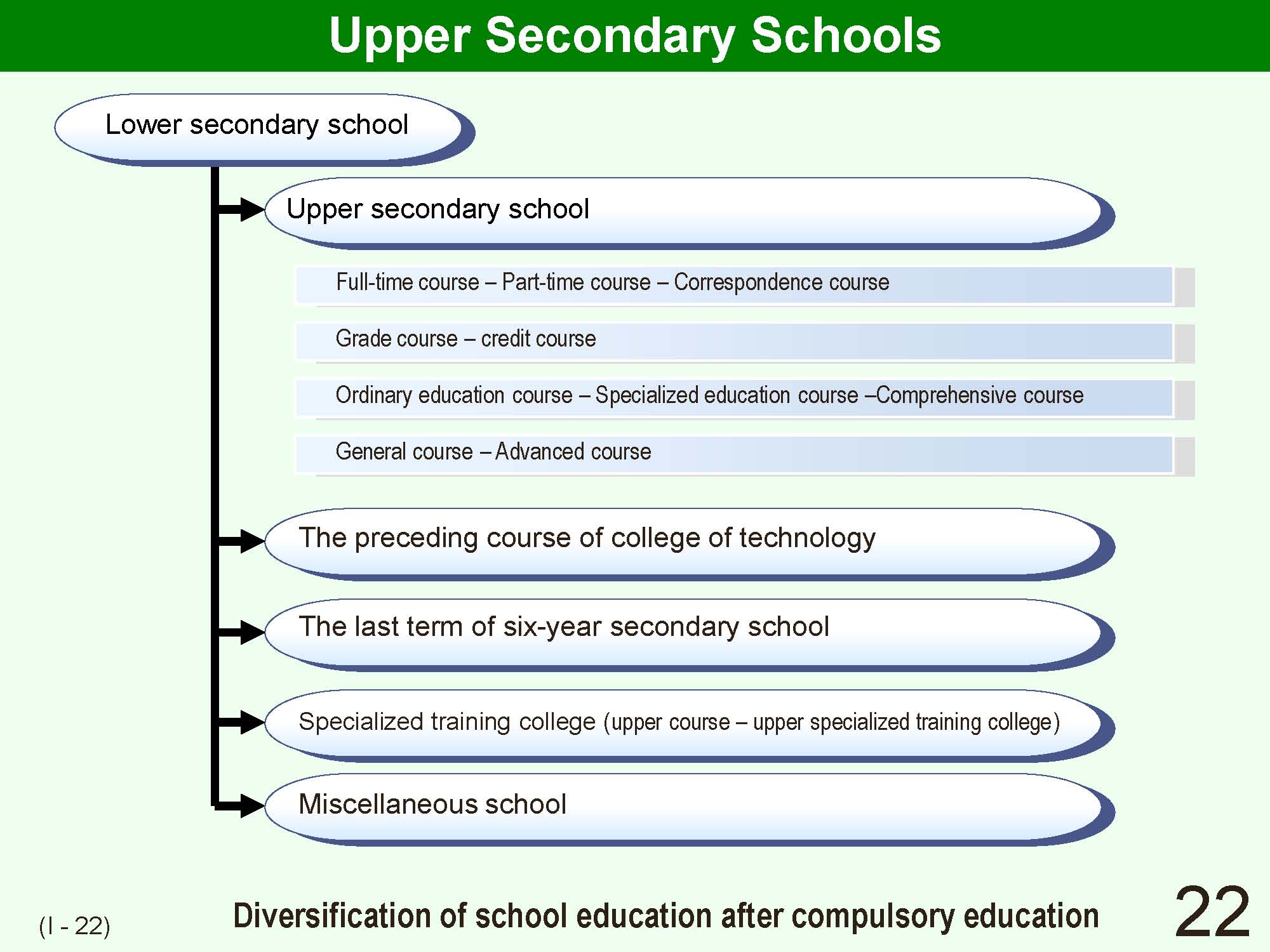
| Education which addresses the needs of studentsf needs and that is relevant to studentsf individual situations has become a basic feature of Japanese education since 97.7% of lower secondary school students receive upper secondary school education after graduation from lower school levels. Therefore diverse educational opportunities are provided following completion of lower secondary schools. These include colleges of technology, upper division of comprehensive six-year-secondary schools, specialized training colleges (upper secondary course]upper secondary specialized training colleges), and miscellaneous schools. This is in addition to the conventional main stream progression from lower secondary schools to upper secondary schools. Moreover, upper secondary schools themselves have been promoting integrated department and credit system schools since they could not accommodate the diverse range of students who go to upper secondary school within the conventional framework of efull time school]part-time coursef and fordinary course]vocational coursef. | ||||
Please send your comments and concerns here
kamada@criced.tsukuba.ac.jp
Center for Research on International Cooperation in Educational Development(CRICED) University of Tsukuba
1-1-1, Tennodai, Tsukuba-shi, IBARAKI
305-857, JAPAN