Frequently Asked Question
The following are the questions frequently raised by the users.
General questions
About function
About graph
Others
How to extract ? The file is downloaded, but ...
- The newest GRAPES is a self-extracting file. After downloading,
double click this file. GRAPES folder will be automatically created, and the files will be extracted there. You can create or move this folder anywhere.
- To start GRAPES, double click the file "grapes.exe" in the GRAPES folder.
About display color
- In 8 bit color (256 colors), GRAPES cannot display its own colors for the after image, for example.
- Use GRAPES in 16 bit color or more.
Natural logarithm and Common logarithm ?
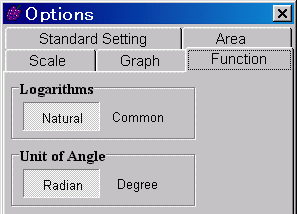 Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)"
Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)"
- If the base is missed, it will be Natural logarithm or Common logarithm.
You can select the logarithm without base (Natural or Common) at "Logarithms" in [Option | Function Options] of the Menu bar. The default is Natural logarithm.
- Ln(x) is also available for natural logarithm.
But there is no button for this, input from keyboard.
Radian measure and Degree measure ?
 The default of GRAPES for measuring angles is radian. The variable in trigonometric functions and their inverses are all in radian.
The default of GRAPES for measuring angles is radian. The variable in trigonometric functions and their inverses are all in radian.
- To change from radian to degree, select at [Option | Function Options] of the Menu bar.
- After this change, the trigonometric functions and the inverse functions invalved will be recalculated.
How to draw the graph of a trigonometric function with domain in degrees ?
How to modify the default setting ?
- Selecting [Option | Set Default], the actual state of working is registered as a default. The position of window and its size will be also registered.
- Example :
To draw the graph of a trigonometric function with domain of degrees, switch from radian to degree. Then, for example, select [Option | Set Default] with the range -100 < x < 100 , -2 < y < 2.
How to draw locus ?
How to change the color and thickness of a segment ?
How to draw the intersection of two or more areas ?
I got an incorrect graph of a relation. Why ?
- To find a point where f (x, y) = 0, GRAPES looks for the point where the sign changes. Therefore, if the sign changes but the value is not 0 (i.e. discontinuous), like tangent or boundary functions,
GRAPES draws a frontier which should not exist.
- You resolve this problem by multiplying the expression by the product of all denominators.
Example : if x = 1/y, write it as xy = 1.
I got an incorrect graph of a polar equation. Why ?
- You resolve this problem by multiplying the expression by the product of all denominators.
Example : if r = 1/(1 - 2 cos θ), write it as r (1 - 2 cos θ) = 1.
- If a polar equation has a relation form, the argument θ discontinuously changes when crossing from the positive part of the x-axis. Because of this, on the positive part of the x-axis, the curve is sometimes drawn incorrectly.
- The radius can have only nonnegative value. If you want anywise to draw a graph with a negative radius, draw two graphs like, for example, r = f (θ) and -r = f (θ - π), for r = f (θ).
How to display a vertical strip indicating a domain ?
Two ways are possible.
- Define regions by inequalities.
- Set the domain for relation like "a <= x <= b".
The region is covered with a hatching pattern like oblique lines.
- Use the rectangle produced by connectting points.
The manipulation is a little complicated, but the representation is very rapid.
- At first, draw a vertical line "A : x = a" as an elementary object.
- Draw a point "B (b, 1)". The y coordinate can have any value.
- Draw a segment from the point B to the vertical line A.
- In the Properties of Line & Polygon, select the rectangle as a line type, the color, and the hatching pattern.
- The vertical strip will be shown with this operation.
- Open the Properties of this point B, and change the object from point to vertical line.
How to draw a triangle and a quadrangle !
- First, draw vertices (points of an elementary object, such as center of circle or just a single point).
- Connect each two points in the same way as for the segment.
- Add the remaining vertices by going to the Properties of Line & Polygon.
How to show the expression in the Graph area ?
How to show coefficients of a polynomial using parameter as a numerical value ?
For example, to display "y = 2x + 3" for the expression "y = ax + b" for "a = 2 and b = 3",
- Open the Note window.
- Write {y = !{a}x + !{b}}
That's all. In the Note, the function is shown following the parameter.
- If the expression to be shown is 6th or less degree function, input "?{expression}".
For example, input "?{ax + b}" for the example shown above.
How to plot a point on the screen without restriction ?
Here is an explanation how to plot a point anywhere on the screen and how to put off the after images resulted from moving this point.
- Select [Set Point] at the position you want to plot, from the menu shown by right click.
(we use the point "P" for the explanation here)
- Click the elementary object "P", and display the Properties of "P".
Configure for making after images. At this time, you can also change the color and the size of point.
- Drag the point "P" in the Graph area.
The point "P" is replaced and the after image remains at the last position.
How to paste the drawn graph to another software such as a word processor ?
Copy the graph drawn to the clipboard, and paste it in anywhere else you wish.
- At first, copy the graph. two ways are possible.
- Click the copy button of the Tool bar on the Data Panel.
- Select "copy" from the popup menu by right click on the graph window.
- You can paste the high quality graph without jagged.
Click the triangle on the right side of the copy button on the Data Panel and select [Graph (Hi-res Col.)] or [Graph (Hi-res B/W)]. You can now paste the graph without jagged, as a vertorial data.
- Then, paste it at the position you want in another software.
Usually, the command "Paste" is in the menu "Edit". See the manual of the software you are using for more detail about "paste".
I can't print the graph. What shoul I do ?
With some printers (especially laser printer), the graph would not be printed in the hi-resolution mode.
The symptom and its solution may vary from one printer to the next.
You may find some of the following useful :
- Draw all graphs in black (select "Graph (hi-res B/W)")
- In the printer properties, select the image mode for the print mode.
- In the printer properties, increase the gray scale of the printer.
Why does paste make the edge of dotted line or broken line "round" ?
- You can select the form of the edge of a segment "round"
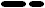 or "sharp"
or "sharp" 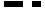 .
.
- In the "sharp" mode, you can print correctly from GRAPES. But, if you copy and paste to another software, it becomes round (I don't know why. Because of the system of Windows ?).
The spaces between the segments for "round" and "sharp" are different. So, if you want to paste to another software, it will be better to be in the "round" mode.
| Display and print in the "sharp" mode |
 |
| Paste in the "sharp" mode |
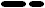 |
| Display, print, and paste in the "round" mode |
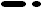 |
 Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)"
Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)" Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)"
Logarithmic function should be written in the form "log (base, argument)" The default of GRAPES for measuring angles is radian. The variable in trigonometric functions and their inverses are all in radian.
The default of GRAPES for measuring angles is radian. The variable in trigonometric functions and their inverses are all in radian.